How NIST AI Framework Can be Used for ISO/IEC 17024 Compliance

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is beginning to reshape certification processes from job analysis and test development to exam health checks. While these tools offer speed and efficiency, they also introduce new risks around validity, reliability, and transparency.
The revised ISO/IEC 17024 standard (likely publication January 2026) is expected to include new requirements for certification bodies that use AI in certification activities. The revision sets requirements at a high level, outlining what must be achieved but not prescribing how it should be implemented. Certification bodies will therefore need to interpret and operationalize these requirements within their own systems and processes.
In this context, the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) offers a practical roadmap. By aligning AI adoption with NIST’s framework, certification bodies can strengthen confidence in their processes and demonstrate compliance with ISO/IEC 17024 expectations.
The revision also makes one principle clear: if AI is used in certification, it must be trustworthy, transparent, and subject to human oversight. AI should be seen as a supportive tool that enables more informed decisions, not as an autonomous agent that replaces human judgment.
ISO/IEC 17024: New Requirements for AI Use
Following requirements from the Draft ISO/IEC 17024 standard relates to the use of AI systems.
- Verify, manage and monitor AI to ensure intended results.
- Validate outcomes of AI with subject matter experts (SMEs).
- Ensure personnel have the necessary competence in the oversight and use of AI.
- Provide human oversight of AI.
- Demonstrate the validity, reliability and fairness of the use of AI.
- Disclose its use of AI and obtain acknowledgement.
Why Certification Bodies Need a Framework
Certification bodies operate in high-stakes environments. Decisions based on flawed AI outputs could:
- Undermine fairness (e.g., bias in job analysis or exam development)
- Compromise reliability (e.g., inconsistent exam health monitoring)
- Erode trust (e.g., lack of transparency in how AI contributes to outcomes)
Applying the NIST AI Risk Management Framework
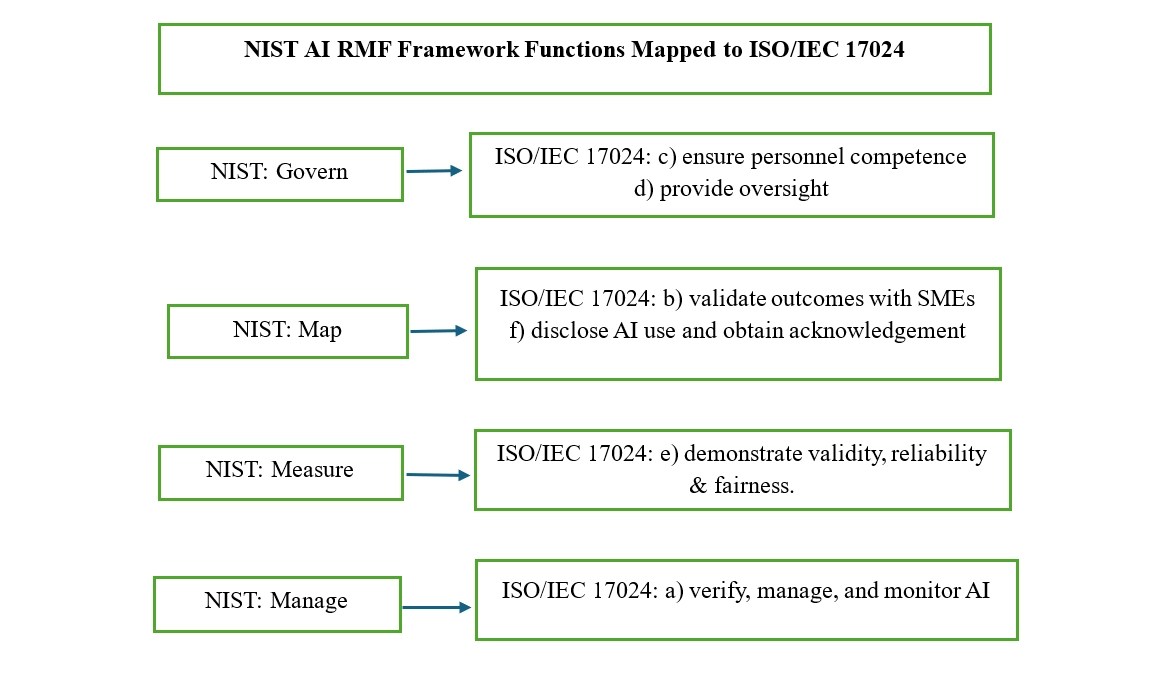
The NIST AI RMF organizes trustworthy AI into four functions: Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage. Certification bodies can use these functions to align with ISO/IEC 17024’s new requirements.
1. Govern: Set Policies and Responsibilities
- Establish an AI oversight committee within the certification body.
- Define clear responsibilities for AI selection, monitoring, and validation.
- Document governance policies for AI use across certification activities (e.g., test development, psychometric analysis, exam security monitoring).
ISO/IEC 17024 link: Supports clauses (c-personnel competence in use of AI), (d- human oversight),
2. Map: Understand Context and Intended Use
- Define the scope and purpose of AI systems (e.g., AI is used to generate draft test items, which are then reviewed by human SMEs).
- Identify risks and stakeholders, including candidates, employers, and regulators.
- Map data flows: where training data comes from, how it is processed, and where outputs are applied.
- Disclose AI use and obtain acknowledgement where candidates interact with AI.
ISO/IEC 17024 link: Supports clauses: b- SME validation, f-disclosure and acknowledgement.
3. Measure: Evaluate and Document Performance
- Conduct validity and reliability studies on AI-assisted outputs (e.g., consistency of item difficulty, fairness across demographic groups).
- Apply bias and fairness audits to ensure exam content does not disadvantage specific populations.
- Maintain documentation and test results as auditable evidence.
ISO/IEC 17024 link: Supports clause: e- validity, reliability, fairness.
4. Manage: Monitor and Improve Over Time
- Set up continuous monitoring of AI tools (e.g., exam health checks, performance drift detection).
- Require periodic re-validation of AI systems, similar to how human examiners must demonstrate ongoing competence.
- Establish a feedback loop where anomalies trigger human review and corrective action.
ISO/IEC 17024 link: Supports clause: a-verify, manage, monitor.
Documentation and Evidence: A Practical Checklist
Certification bodies should maintain a documented record covering:
- AI Governance policies (roles, responsibilities, risk acceptance)
- System descriptions (purpose, data sources, limitations)
- Validation and reliability studies (psychometric evidence, bias audits)
- Monitoring protocols (frequency, triggers for intervention)
- Competence records (training of staff overseeing AI tools)
- Candidate disclosures and acknowledgements (aligned with clause f)
This evidence should help meet ISO/IEC 17024 compliance and reinforce credibility with stakeholders.
Conclusion: Trust Through Transparency
Certification bodies cannot treat AI as a black box. Instead, by leveraging the NIST AI RMF, they can establish governance, map risks, measure validity, and manage performance over time.
With the upcoming revision of ISO/IEC 17024, certification bodies that proactively align their AI practices with these principles will be better positioned to demonstrate compliance and maintain the trust of candidates, employers, and regulators in a rapidly evolving landscape.






