As digital technology rapidly evolves, the role of electronics in our day to day lives and industries becomes vaster and more usable. Flexible printed electronics enable compact, bendable, and portable designs, but they require specialized testing technologies. IPC-9257, Requirements for Electrical Testing of Flexible Printed Electronics is intended to assist in selecting the test equipment, test parameters, test data, and fixturing required to perform electrical test(s) on flexible printed electronics.
What Are Flexible Printed Electronics?
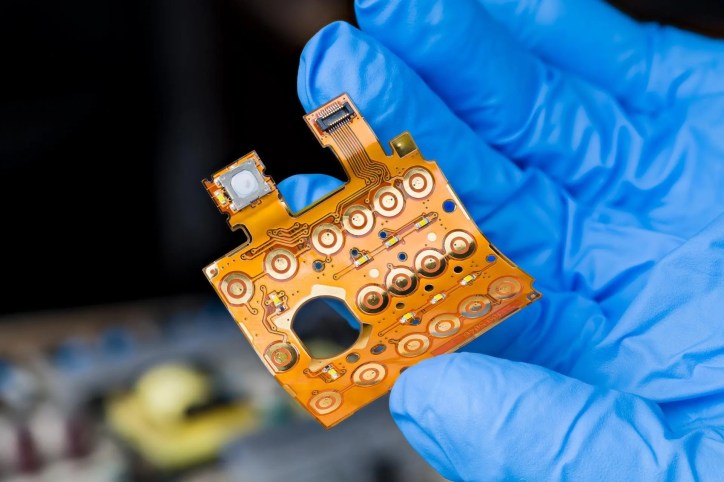
Flexible printed electronics are electronic circuits built on flexible, stretchable, or conformable substrates like plastic, paper, or even metal foil. These circuits are typically created using printing methods, such as inkjet or screen printing, making them cost-effective and enabling mass production. This technology opens up possibilities for new product designs and functionalities, like flexible displays, wearable devices, and smart packaging. Flexible electronics can help make an existing product smaller, lighter, and more pliable.
The unique characteristics of flexible printed electronics, such as their ability to bend and stretch, require specific testing methods to validate their functionality under various conditions.
What Is the Purpose of Testing Flexible Printed Electronic?
The main objective of electrical testing for flexible printed electronics—such as wearables, smart packaging, and medical devices—is to assure their safe and reliable operation. Rigorous electrical testing involves inspecting, evaluating, and monitoring electrical installations to identify potential hazards and assure compliance with safety standards. According to IPC-9257, electrical testing verifies that the conductive networks on the flexible printed electronics are interconnected according to the design requirements.
The standard does note, however, that many physical characteristics of the conductors (e.g., dimensional accuracy, conductor geometry and registration, presence of holes) cannot be determined by electrical test, so other checks should be employed to confirm these characteristics.
What Is IPC-9257?
IPC-9257 outlines the requirements for electrical testing of flexible printed electronics. It specifies test equipment, parameters, data collection, and fixturing methods to assure that the flexible printed electronics product meets the electrical design criteria detailed in IPC-6902. The IPC-9257 standard also defines different levels of testing.
Uses of Flexible Printed Electronics
Flexible printed electronics find use in a wide array of applications, leveraging their ability to be both flexible and printed on various substrates. These include flexible displays, RFID tags, smart textiles, in-mold electronics, and a variety of sensors and biosensors. They also play a crucial role in consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial application. Here are a few examples of how flexible printed electronics are used:
- Sensors and Biosensors: Flexible sensors are used for a variety of applications, including light, temperature, pressure, and even biosensors that can detect bodily fluids.
- Smart Packaging: Flexible electronics can be used in smart packaging, such as RFID antennas on delivery boxes, for tracking and monitoring.
- Consumer electronics: Smartphones, tablets, and wearables utilize flexible circuits for their compact designs and ability to fit in curved spaces
- Medical Devices: Flexible printed circuit boards are used in hearing aids, cochlear implants, and implantable medical technology due to their miniaturization and biocompatibility.
- Continuous Health Monitoring: Flexible sensors can be worn discreetly on the skin to provide real-time data on vital signs, allowing for continuous health monitoring.
- Automotive: Flexible circuits are used in automotive electronics for connecting components across hinges, doors, and seats, and in safety systems like airbag deployment.
- Wearable Technology: Flexible electronics enable the creation of wearable devices like e-textiles with integrated sensors, flexible batteries, and displays.
IPC-9257, Requirements for Electrical Testing of Flexible Printed Electronics is available on the ANSI Webstore.